The Marketing Plan: How to Design and Control It
A marketing plan is an essential tool for any business seeking to achieve its marketing objectives and ensure growth and success in the market.
In my postgraduate marketing studies at Douglas College, we are studying the book A Framework for Marketing Management by Kotler and Keller. In this post, we will explore in detail what a marketing plan includes and how to monitor and improve it.
What Does a Marketing Plan Include?
A marketing plan is a written document that summarizes what the marketer has learned about the market and how the company plans to achieve its marketing objectives. According to the book Marketing Management by Philip Kotler and Kevin Lane Keller, a marketing plan typically contains the following sections:
1.1 Executive Summary and Table of Contents
The executive summary provides an overview of the main goals and recommendations of the plan. It is crucial for quickly capturing the attention of executives and giving them a clear understanding of what is expected to be achieved. The table of contents makes it easy to navigate through the document, allowing readers to quickly find the information they need.
1.2 Situation Analysis
The situation analysis presents relevant data on sales, costs, market, competitors, and the macro environment. It includes a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to better understand the market environment. This analysis is fundamental to identifying the company’s internal capabilities and external threats and opportunities.
Market Analysis
Examine current market trends, market size, market growth, and market segments.
Competitor Analysis
Evaluate direct and indirect competition, including their strengths and weaknesses.
Environmental Analysis
Consider external factors such as the economy, legislation, technology, and sociocultural trends that may affect the business.
Internal Analysis
Evaluate the company’s resources, capabilities, and core competencies.
1.3 Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy defines the mission, marketing and financial objectives, and how the product or service will meet market needs. This includes market segmentation, target market selection, and product positioning.
Mission Definition
The mission statement should explain the business’s purpose and guide strategic decisions.
Marketing and Financial Objectives
Specific goals the company wants to achieve, such as increasing market share, launching new products, or improving profitability.
Market Segmentation
Divide the market into distinct segments of customers with similar needs, characteristics, or behaviors.
Target Market Selection
Choose one or more market segments to target.
Product Positioning
Define how the product will be differentiated in consumers’ minds compared to competitors’ products.
1.4 Marketing Tactics
Marketing tactics describe the marketing activities to be carried out to execute the strategy, including decisions about the product, price, channels, and communication.
Product Decisions
Product features, design, quality, branding, and packaging.
Pricing Strategies
Determine the right price for the product, considering costs, demand, and competitors’ prices.
Distribution Channels
Choose the most effective channels to bring the product to the target market.
Communication and Promotion
Advertising, public relations, personal selling, promotions, and digital marketing strategies.
1.5 Financial Projections
Financial projections include a sales forecast by month and product category, an expense forecast, and a break-even analysis to determine how many units must be sold to cover fixed and variable costs per unit.
Sales Forecast
Estimate future sales based on historical data, market trends, and marketing objectives.
Expense Forecast
Estimate the costs associated with marketing and operational activities.
Break-even Analysis
Calculate the sales volume needed to cover all costs and start generating profits.
1.6 Implementation Controls
Implementation controls detail the controls to monitor and adjust implementation activities. This section typically sets monthly or quarterly goals and budgets so management can review results and take corrective action if necessary.
Goals and Budgets
Set specific objectives and allocate financial resources to achieve them.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of marketing activities.
Corrective Measures
Adjust strategies and tactics based on results and market feedback.
2. ¿How to Monitor and Improve a Marketing Plan?
Monitoring and improving a marketing plan is crucial to ensure that the implemented strategies are working effectively and to make adjustments when necessary. Kotler and Keller suggest several tools and methods for this purpose:
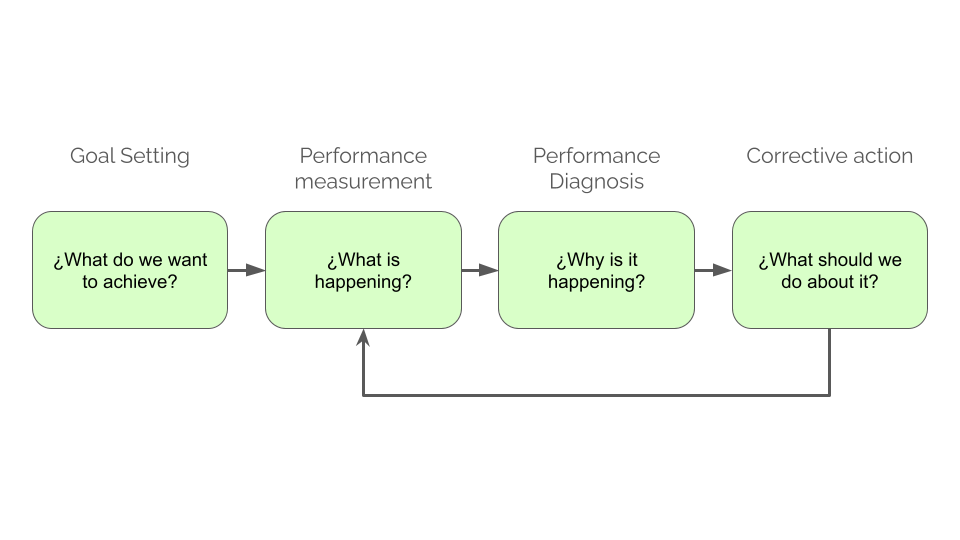
2.1 Marketing Implementation
Marketing implementation is the process of turning marketing plans into action assignments and ensuring that the set objectives are achieved. This includes budgets, schedules, and marketing metrics to monitor and evaluate results over time.
Marketing Budgets
Allocate financial resources to various marketing activities.
Schedules
Establish a timeline to ensure all actions are carried out on time.
Marketing Metrics
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of marketing campaigns.
2.2 Marketing Metrics
Marketing metrics are a set of measures that help marketers quantify, compare, and interpret their performance. These can include sales growth, market share, purchase intention, and repurchase rate.
Sales Growth
Measure the increase in sales over a specific period.
Market Share
Evaluate the company’s market share compared to competitors.
Purchase Intention
Measure the likelihood of consumers buying the product in the future.
Repurchase Rate
Evaluate the frequency with which customers repeat the purchase of the product.
2.3 Marketing Mix Modeling
Marketing mix modeling involves analyzing data from various sources to understand the effects of specific marketing activities. This helps companies allocate or reallocate marketing expenses more precisely.
Data Analysis
Use analytical tools to evaluate the impact of different marketing activities.
Budget Adjustment
Reallocate the marketing budget based on data analysis results.
2.4 Marketing Dashboards
Marketing dashboards are a structured way to disseminate insights gained from metrics and marketing mix modeling. Dashboards allow management to evaluate the performance of marketing activities and make informed decisions.
Data Visualization
Use charts and graphs to visually represent performance data.
Decision Making
Base strategic decisions on the information provided by marketing dashboards.
2.5 Marketing Audits
Marketing audits are a comprehensive, systematic, independent, and periodic review of a company’s marketing environment, objectives, strategies, and activities. Audits can identify problem areas and opportunities, recommending plans to improve marketing performance.
Systematic Review
Evaluate all marketing areas to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Recommendations
Provide suggestions for improving marketing strategies and tactics.
Action Plan
Develop a detailed plan to implement audit recommendations.
2.6 Feedback and Adjustment
Constant feedback from customers and the marketing team is essential to adjust the plan as necessary. This can include customer satisfaction surveys, team meetings, and ongoing performance analysis.
Customer Satisfaction Surveys
Gather customer opinions about their experiences and perceptions of the product.
Team Meetings
Facilitate communication and collaboration among marketing team members.
Continuous Analysis
Conduct periodic reviews of marketing plan performance to identify areas for improvement.
In conclusion, a well-structured and monitored marketing plan is vital for the success of any business. By following these steps and using the right tools, companies can adapt to market changes and continuously improve their marketing strategies. A marketing plan is not a static document; it must be reviewed and adjusted regularly to reflect changing market conditions and new business opportunities.
Juan Esteban Yepes
